
A condom can hold up to 7 GALLONS of fluid.
SOURCE: OMG-FACTS.COM
Here, you'll find answers to your birth control questions plus resources you need to be informed, get prepared, and find the birth control method that works best for you.
A condom can hold up to 7 GALLONS of fluid.
SOURCE: OMG-FACTS.COM
14% OF PILL USERS rely on birth control for reasons other than contraception.
SOURCE: GUTTMACHER.ORG

A more permanent option for those who are sure they don’t want a future pregnancy.
Learn More >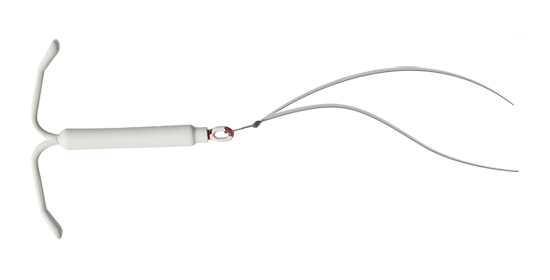
IUDs are long lasting and won’t interrupt the moment – and are either hormonal or non-hormonal.
Learn More >
There’s nothing to think about in the moment and it’s hidden from everyone.
Learn More >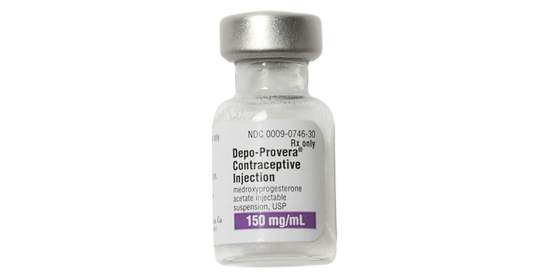
Long-lasting, private, and a hormonal choice for those who can’t take estrogen as it’s a progestin only method.
Learn More >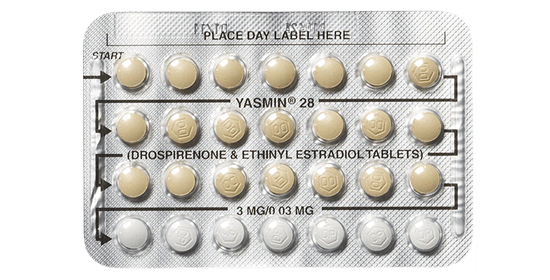

Easy to insert, works like the pill, keeps you protected for a month at a time.
Learn More >
Easy to use and works like the pill, but you only have to worry about it once a week. Just remember, the patch does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Learn More >
They reduce the risk of STIs, don’t require a prescription, easier to find and are inexpensive.
Learn More >
Emergency Contraception provides the possibility of prevention after you have sex.
Learn More >

Immediately effective, no hormones, can be inserted up to 6 hours before sex. Just remember, the cervical cap does not protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Learn More >
Immediately effective, no hormones, can be inserted up to 6 hours before sex.
Learn More >
No hormones, no prescription, and can be inserted up to 24 hours before sex. Just remember, the sponge does not protect against sexually transmitted infections
Learn More >

Withdrawal doesn’t cost a dime or require a visit to the doctor, but you get what you pay for.
Learn More >